We know switch having one broadcast domain and multiple collision domain.In normal case when a switch sends a broadcast it will reach all ports.But in some cases we have to restrict that behavior of switches.For that we use Virtual LANs (or VLANs).
VLAN's separate a Layer-2 switch into multiple broadcast domains. Each VLAN is its own individual broadcast domain.Individual ports or groups of ports can be assigned to a specific VLAN. Only ports belonging to the same VLAN can freely communicate to each other.
A router or layer 3 switch is needed for Inter-VLAN Communication.Broadcasts from one VLAN will never be sent out ports belonging to another VLAN. By default on Cisco Catalyst switches, all interfaces belong to VLAN 1.
VLAN 1 is considered the Management VLAN (by default). What are the advantages of using vlans?
What are the advantages of using vlans?
• A VLAN is a single broadcast domain which means that if a user in the engineering VLAN sends a broadcast frame only users in the same VLAN will receive it.
• Users are only able to communicate within the same VLAN (unless you use a router).
• Users don’t have to be grouped physically together, as you can see we have users in the Engineering vlan sitting on the 1st, 2nd and 3rd floor.
Terminologies associated with VLAN'sTrunking : Carrying multiple VLANs over the same physical connection.We must configure a trunk link between two switches.Only trunk links are capable of carrying multiple VLAN information
Native VLAN :By default, frames in this VLAN are untagged when sent across a trunk. VLAN 1 is called native VLAN (By default)
Access VLAN : The VLAN to which an access port is assigned
Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) :Can be used to automatically establish trunks between capable ports (insecure method!)
Switched Virtual Interface (SVI) : A virtual interface which provides a routed gateway into and out of a VLAN
Router on Stick : Method used for communicating Inter-VLAN's using a router
There are two trunking protocols we can use:
•
IEEE 802.1Q [dot1Q] : An open standard that is supported on switches from many vendors and most NICs.
•
Cisco ISL (Inter-Switch Link): An old Cisco proprietary protocol that is only supported on some Cisco switches.
IEEE 802.1QISL (Inter-Switch Link)
Open Standard
Cisco Proprietary
Native VLAN is not tagged
Native Vlan is tagged
Tags Ethernet Frame
Encapsulate Ethernet Frame
Maximum VLANs : 4094
Maximum VLANs 1000
Header Size : 4 bytes
Header Size : 26 bytes
Different Switch Port ModesTrunk : Forms an unconditional trunk
dynamic desirable : Attempts to negotiate a trunk with the far end
dynamic auto : Forms a trunk only if requested by the far end
access : Will never form a trunk
Let me give you an overview of the different switchport modes and the result:
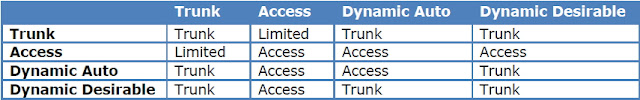 Note :
Note : Older switches are dynamic desirable by default and modern switches are dynamic auto by default.Its better to manually configure trunk and give non-negociate command.The negotiation of the switchport status by using dynamic auto or dynamic desirable is called DTP (Dynamic Trunking Protocol). You can disable it completely by using the switchport nonegotiate command
VLAN information is not saved in the running-config or startup-config but in a separate file calledvlan.dat on your flash memory. If you want to delete the VLAN information you should delete this file by typing delete flash:vlan.dat.VLAN Creation
Switch(config)# vlan 100
Switch(config-vlan)# name Engineering
Switch(config-vlan)#exit
Adding interface to VLAN
Switch(config)#interface fastethernet 0/1
Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access
Switch(config-if)# switchport nonegotiate
Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 3
Configuring Trunk Links
To manually configure a trunk port, for either ISL or 802.1Q tagging:
Switch(config)#
interface fa0/24Switch(config-if)#
switchport trunk encapsulation< isl / dot1q >Switch(config-if)#
switchport mode trunkSwitch(config-if)# switchport nonegotiateTo change Native Vlan
Switch(config)#
interface fa0/14
Switch(config-if)#
switchport trunk native vlan 100
For security reasons it might be a good idea not to allow all VLANs on your trunk link. We can change this by using the
switchport trunk allowed vlan command.
Switch(config)# interface fa0/24
Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan remove 50-100
Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan add 60-65
The first switchport command will prevent the trunk port from passing traffic from VLANs 50-100. The second switchport command will re-allow the trunk port to pass traffic from VLANs 60-65.
SVI Configuration
Switch(config)# interface vlan100
Switch(config-if)# ip address 192.168.100.1 255.255.255.0
Router on a Stick ConfigurationSTEP 1 : Switch configuration
SW1# configure terminal
SW1(config)# interface fa 0/1
SW1(config-if)# switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
SW1(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
The above steps complete the switch-side configuration.
STEP 2 - Router Configuration
We need to follow a similar configuration for our router to enable communication with our switch and allow all VLAN traffic to pass through and route as necessary.
R1# configure terminal
R1(config)# interface Fa 0/2
R1(config-if)# no ip address
R1(config-if)# no shutdown
R1(config-if)# interface Fa 0/2.1
R1(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1q 1 native
R1(config-subif)# ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-subif)# interface Fa 0/2.2
R1(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1q 2
R1(config-subif)# ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-subif)#exit
Show Commands
show vlan
show interface fa 0/24 switchport]
show interface trunk
show interface fa 0/24 trunk
INTERVIEW QUESTIONS
- Which switching technology reduces the size of a broadcast domain?
- Which protocols are used to configure trunking on a switch?
- What is SVI ?
- what is meant by "router on stick" ?
- which is the default mode in switch ports ?
- Difference between 802.1Q and ISL ?
- Which are the two trunking protocols ?
- Which Protocol encapsulate Etherframes ?
- Which is the Vlan not tagged by 802.1Q ?
- How to delete vlan information from switch ?
- Difference between access and trunk mode ?
- Difference between dynamic auto and dynamic desirable ?
- what is the use of nonegociate command in switch ?
- Explain different switch port modes ?
- what is DTP ?
- Can we see trunk interfaces in show vlan command ?
- which is the command used to see trunk interfaces ?
- what is the maximum number of vlans permitted in 802.1Q and ISL
- what is the header size of 802.1Q ?